NAD+の新規な前駆体,Nicotinamide ribosideとは
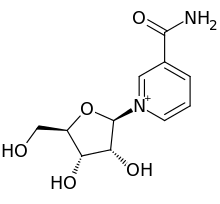

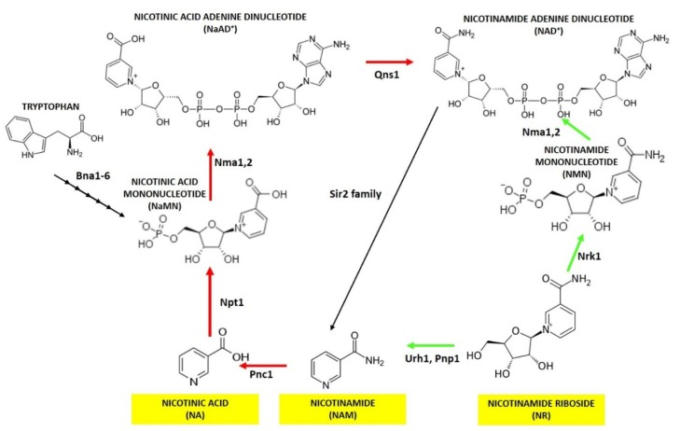
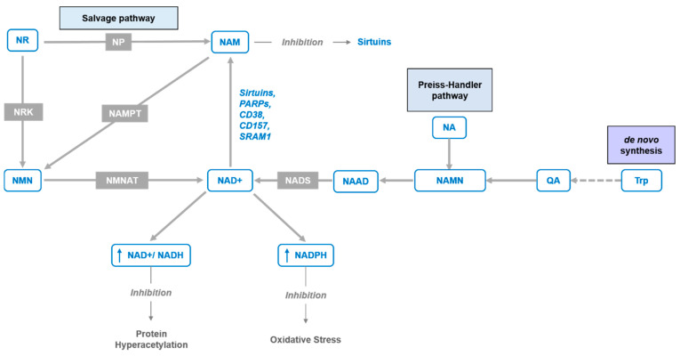
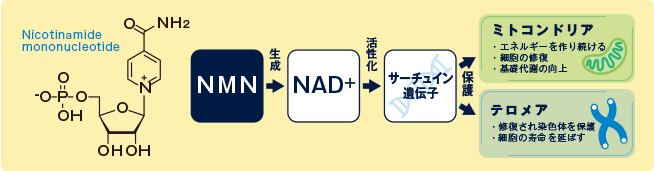
Nicotinamide riboside (NR, SR647) is a pyridine-nucleoside and a form of vitamin B3. It functions as a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, or NAD+,[1] through a two-step and a three-step pathway. NRはピリミジンヌクレオチド(五炭糖+核酸)で、ビタミンB3ともいわれる NADの前駆体の一つ
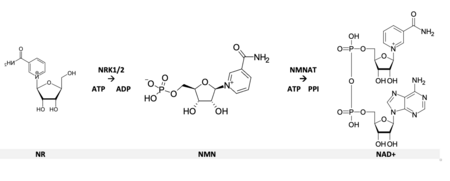
The identification of Nicotinamide riboside (NR) as an NAD precursor in eukaryotes developed out of the study of pellagra.
Pellagra was the first disease to be associated with NAD+ deficiency.[11] It was linked to nutritional deficiency by Joseph Goldberger in 1914, and to deficiency of niacin (vitamin B3) by Conrad Elvehjem in 1937.
NAD+ (then called coenzyme I) was shown to be extremely low in cases of pellagra, and NA and NAM were identified as molecular precursors in rebuilding NAD+ levels.
Pellagra is now understood as a severe, chronic depletion of NAD+, which can be treated through diet.